Understanding 90 Degrees of Shoulder Flexion: Importance and Implications
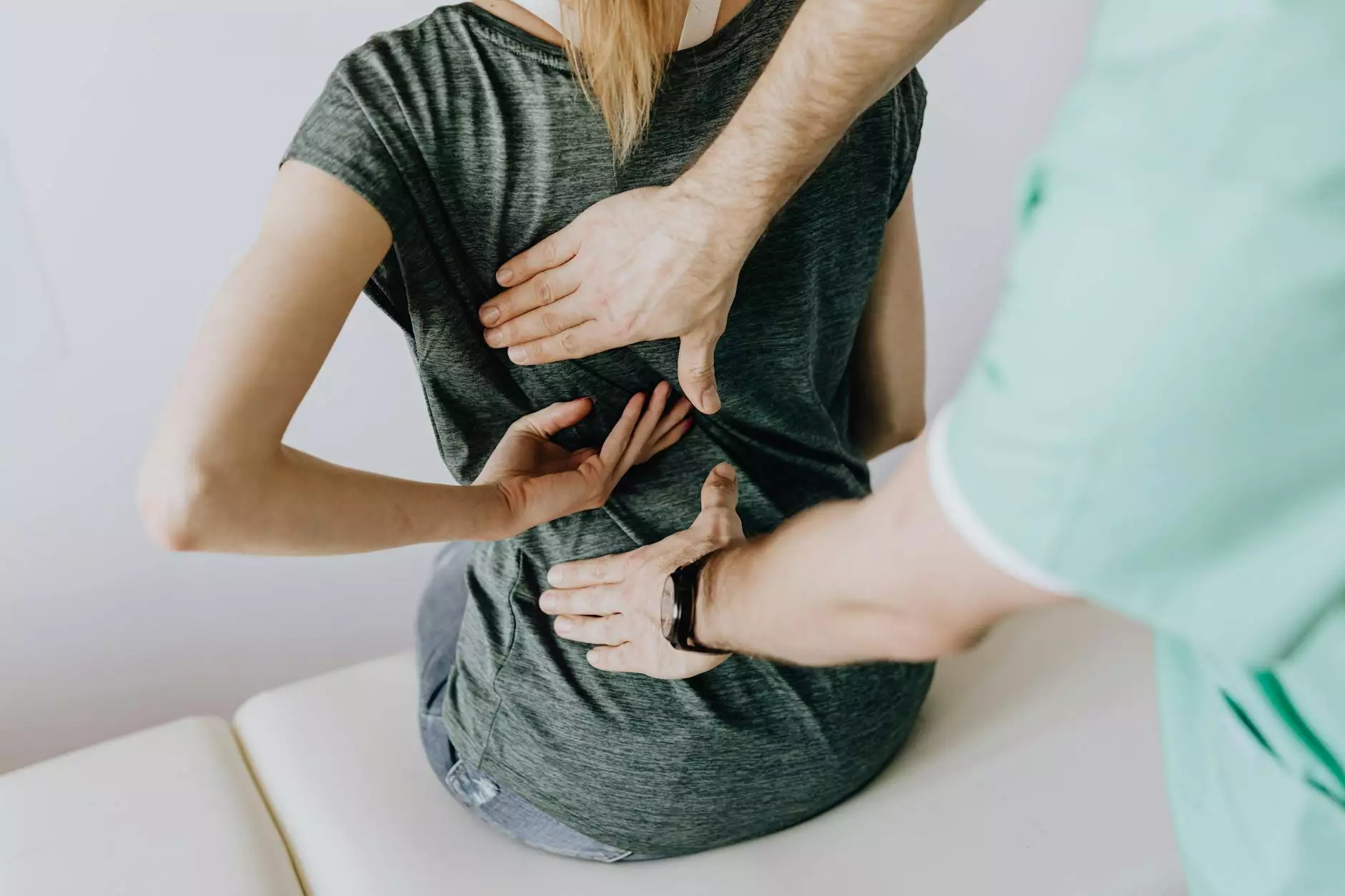

When it comes to shoulder mobility, one crucial measurement often discussed among health professionals, especially in chiropractic and rehabilitation, is the term "90 degrees of shoulder flexion". This article delves deep into the significance of this angle, the biomechanics involved, and its relevance to various fields such as health, medical diagnosis, and rehabilitation therapies.
What is Shoulder Flexion?
Shoulder flexion refers to the movement that raises the arm in front of the body toward the head. It is an essential motion necessary for everyday activities such as reaching, lifting, and throwing. Understanding the mechanics of shoulder flexion allows healthcare providers to better diagnose and treat shoulder-related ailments.
The Anatomy of the Shoulder
The shoulder joint, known as the glenohumeral joint, is one of the most mobile joints in the human body. It consists of bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments which work together to allow a wide range of motion. The major components include:
- Humerus: The upper arm bone that forms the ball of the shoulder joint.
- Scapula: The shoulder blade that provides structure and support.
- Clavicle: The collarbone that connects the arm to the body.
- Rotator Cuff: A group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder.
The Significance of 90 Degrees of Shoulder Flexion
Achieving 90 degrees of shoulder flexion is often viewed as a benchmark in both therapeutic and athletic settings. Why is this angle so important? Here are some key reasons:
1. Functionality
For many daily activities, 90 degrees of shoulder flexion allows individuals to perform essential tasks, such as placing items on high shelves or reaching overhead. This functional capacity is critical for maintaining independence in older adults and enhancing performance in athletes.
2. Assessment of Injuries
Injury assessment often includes measuring the range of motion. Health practitioners, especially chiropractors and physical therapists, assess whether a patient can achieve 90 degrees of shoulder flexion, as limited mobility could indicate potential injuries such as rotator cuff tears or shoulder impingement syndrome.
3. Rehabilitation Milestones
In rehabilitation programs, achieving 90 degrees of shoulder flexion is typically a goal for patients recovering from shoulder surgery or injury. Tracking progress to this milestone allows therapists to adjust therapy techniques and ensure effective recovery.
Measuring Shoulder Flexion
Measuring shoulder flexion can be done through various methods, including goniometers and digital inclinometers. The following steps illustrate how a physical therapist might measure shoulder flexion:
Step-by-Step Measurement with a Goniometer:
- The patient should stand or sit comfortably, ensuring that the spine is aligned.
- The therapist positions the goniometer with the center over the shoulder joint.
- The arm is raised forward to measure the angle of flexion.
- The measurement is noted, ideally achieving or exceeding 90 degrees for optimal function.
Factors Affecting Shoulder Flexion
Several factors can influence a person's ability to achieve 90 degrees of shoulder flexion. Understanding these factors is crucial for health practitioners when developing treatment or rehabilitation plans.
- Age: As individuals age, flexibility can decrease, making it more challenging to reach full shoulder range.
- Injury History: Previous injuries can lead to reduced mobility due to pain or structural changes in the shoulder.
- Muscle Strength: Weakness in shoulder or surrounding muscles can result in limited motion.
- Joint Health: Conditions such as arthritis can significantly reduce range of motion.
Improving Shoulder Flexion
To encourage healthy shoulder flexion, individuals, especially those undergoing rehabilitation, can incorporate specific exercises designed to enhance flexibility and strength in this region. Here are a few recommended practices:
1. Stretching Exercises
Regular stretching can help maintain or improve shoulder flexion. Consider these stretches:
- Arm Across Chest Stretch: Pull one arm across your chest and hold it with the opposite arm.
- Overhead Stretch: Reach both arms overhead while standing tall to elongate the shoulder muscles.
2. Strengthening Exercises
Building strength in shoulder muscles is vital. Incorporate the following:
- Shoulder Press: Use dumbbells or resistance bands to press upward, focusing on form.
- Scapular Retractions: Keep your shoulders down and back to strengthen the muscles around the shoulder blade.
3. Professional Guidance
Working with a chiropractor or physical therapist can provide tailored guidance and exercises suited to specific needs, ensuring effective improvement in shoulder flexion. They can devise a personalized program to aid recovery and prevent future injuries.
Conclusion
Understanding and achieving 90 degrees of shoulder flexion is vital for maintaining functional independence and enhancing athletic performance. Its importance cannot be overstated in rehabilitation, injury assessment, and general mobility.
Healthcare providers and patients alike should prioritize shoulder mobility exercises and seek professional advice if experiencing limitations. This proactive approach not only improves the quality of life but also leads to better health outcomes.
Consulting Experts
For those interested in enhancing their shoulder mobility or recovering from injuries, consider consulting IAOM-US for expert advice and personalized therapy options. Their team specializes in various health and medical fields, ensuring comprehensive support for all patients.
Final Thoughts
Remember that while exercises and stretches can significantly improve shoulder flexion, always consult with healthcare professionals before starting any new exercise regimen—particularly if you have pre-existing conditions or injuries.